Procalcitonin “An ideal biomarker for bacterial infection”
Featured Reagents;
Procalcitonin ( PCT )
An ideal biomarker for bacterial infection should not only allow early
diagnosis, but also inform about the course and prognosis of the disease and guide therapeutic management. Since the first report in 1993 on the association of serum procalcitonin (PCT) levels with bacterial infection 1 there is a solid body of evidence in the literature that this marker is being increasingly recognized as a good marker of bacterial infections and sepsis and therefore as an important tool in clinical practice.
Clinicians should always interpret PCT values in the clinical context of the patient. The increase in PCT reflects the continuous development from a healthy condition to the most severe consequences of bacterial infection (severe sepsis and septic shock). Therefore, optimal cut-off values for PCT are variable and dependent on factors such as the clinical setting, the site and extent of the infection and the presence of co-morbidities.
- Liquid Reagents:
Liquid reagents for enhanced stability - Early Sepsis:
PCT – useful parameter for early sepsis diagnosis
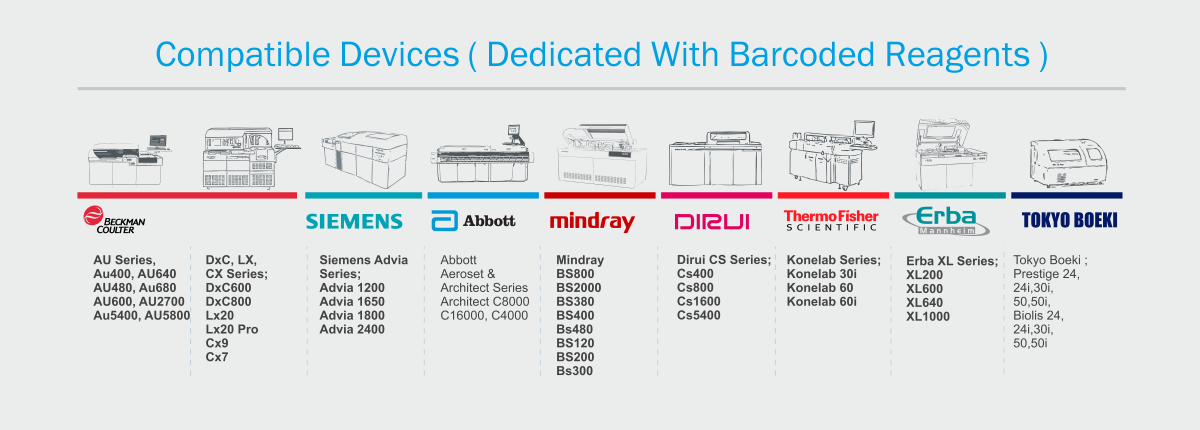
- Completely automated protocols:
Are available for a wide range of analysers ( ready application, and dedicated with barcoded reagents ) - Other features:
Excellent stability of 2 weeks when stored at +2 to +8°C

